Essayist Melissa Ballard contributes the fourth in our series of guest posts here at Rust Belt Girl, and, let me tell you, you’re in for a treat. Melissa has a talent for bringing the past to life and making her ancestors feel like our shared family. In this essay we meet Phyllis, Melissa’s grandmother, a woman of Northern Appalachian Ohio, whom Melissa writes about in a loving yet candid way, deftly delving into what makes personhood–class, sex, education, place and much more. (We also hope Phyllis is having the “time of her life,” Melissa.)
This Woman
by Melissa Ballard
This woman is my grandma, but not yet.
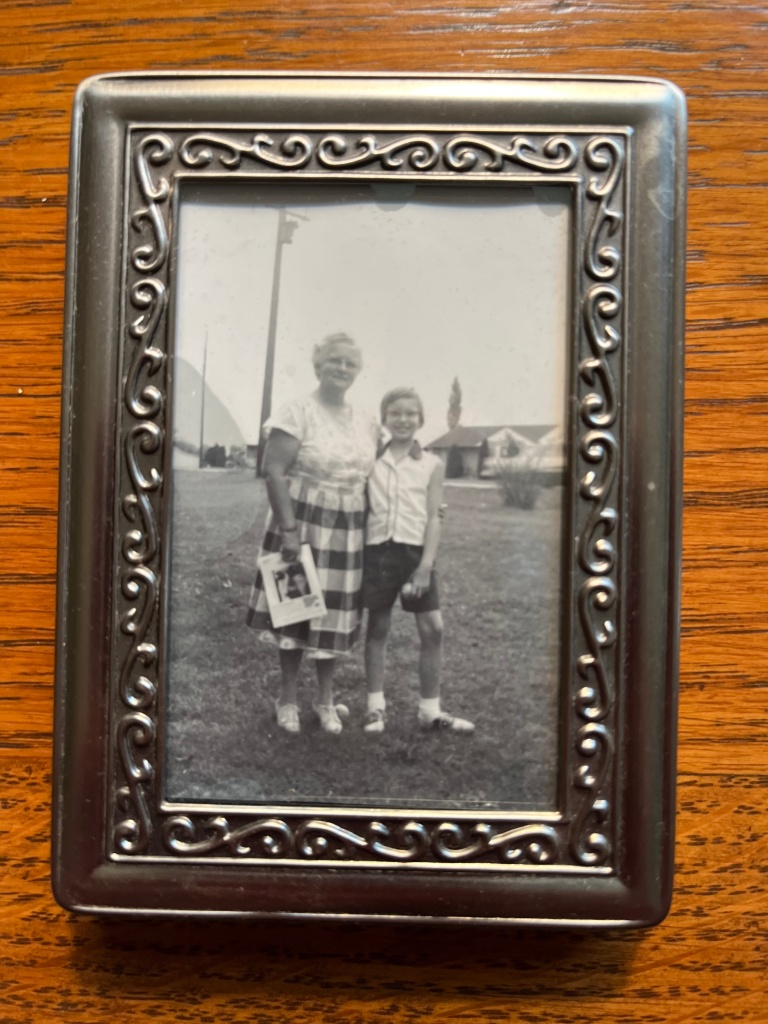
In this black and white photograph, a small, dark hat of woven straw covers her hair and shades her forehead. She wears a walking suit: a jacket and skirt in a light wool pin check with a belt of the same fabric, over a silky, patterned, blouse. The tips of the fingers of her left-hand rest in the pocket of her slim skirt. Her only jewelry is a ring on the little finger of that hand. I can imagine her cropped left foot pointing out, her dark stockings and t-straps. She slouches just a bit and turns her body toward the unidentified photographer. She looks directly at the camera. Her smile is slight, but it reaches her eyes.
This woman’s slight curves contrast with the riveted metal beam, perhaps part of a railroad bridge, that rises at a sharp diagonal behind her. In the early 1920s, her family lived on a side street a few blocks from the train station in Dennison, Ohio. Her father was an inspector for the railroad, so she had a free pass to ride.
This woman could be waiting for the early train to Pittsburgh or Columbus, where she will walk the streets with confidence, on her way to a job interview. But she is not. Or at least I don’t think so. I know little about this brief period, but I hope she is having the time of her life.
In 1925 she has a job in an ice cream shop, lives with her parents. Both she and her mother, who is preoccupied with social status, are named “Margaret.” This woman has already started to express her individuality and goes by her middle name, Phyllis or, on documents, “M. Phyllis.”
On June 18, 1925, eleven days before her nineteenth birthday, Phyllis and her neighbor, Harry, will travel 65.3 miles, maybe by train, to Brooke County, a tapering finger of West Virginia tucked between Ohio and Pennsylvania, where they can get a marriage license with no waiting period. Later that day, they will return to Ohio and be married at the home of the groom’s family.
I wonder whether Phyllis’ parents even attended. They had a reception for her later, but I gather it was her mother’s attempt at saving face. I can’t imagine she approved of my grandpa or his family, and I can easily hear her saying, “He’ll never make a decent living. You’ll end up in the poor house.”
Five months and five days later, their first child will be born. On January 14, 1928, their second child, my dad, will be born.

The woman I remember, my grandma, was in her fifties. She had slim legs but a solid middle. She wore silver, cat-eye glasses before they were retro. Her short, dark hair was streaked with gray and white, her fingernails chewed to the quick. Wearing a well-washed cotton housedress covered with a flowered or checked apron and heavy lace-up shoes, she kept chickens and goats, grew vegetables and flowers, ran the laundry through a wringer before hanging it outside to dry, cooked meals from scratch. She kept a battered pan under the kitchen sink, filling it with food scraps. Every morning she fed it to the three hound dogs Grandpa had brought home from the dog pound, kept in a pen at the back of the yard. “Oh, hush up,” she said as they yipped and howled at her.
When Grandma wasn’t busy with chores, she answered the phone for Grandpa, who was the dog warden. She wrote messages in her flowery cursive: the name, address and phone number of the caller, and a brief description of the stray dog. She followed him to his dark green truck, reading her notes out loud. Grandpa never wrote anything down. Before she finished talking, he was backing out of the long driveway, kicking up gravel as he went.
They lived in a worn-out house on a liminal strip of land in Brightwood, part of Goshen Township, Tuscarawas County; my parents and I had moved to a suburb of Cleveland. Once a month, we made the two-hour trip down home to visit, and I spent more time there during the summer.
On hot afternoons, Grandma and I often sat together on the front porch swing, she doing her mending and me reading, trying to catch a breeze. A two-lane road ran close to the front of the house. The cars seemed to fly by, and the exhaust from the trucks taught me to mouth breathe, a skill I perfected when I ran into the hen house to collect eggs.
This route was nicknamed the “slow road” after a highway, the “fast road,” was built behind the house. One summer Saturday, Grandpa drove us into town on the slow road to get ice cream. Grandma and I sat on a bench with our cones, people-watching while Grandpa ran one of his mysterious errands. If Grandma asked him where he was going, he always said, “I need to see a man about a horse.” Which was odd, because my grandparents didn’t have any horses.
On the way home, I noticed a large house on a hill. “Who lives there?” I asked.
Grandma stiffened. “That’s the poor house. Where you go to live if you don’t have any money. It’s not a nice place.”
I immediately pictured a nineteenth-century orphanage from one of the many books I read. Rows of rusty metal cots with stained mattresses, thin sheets, and scratchy blankets. Peeling paint on crumbling walls. I shuddered and looked away.
…
The dining room at Grandma’s was small, with windows on three sides, some covered in plastic to keep out drafts. It was an afterthought tacked on to one side of the house next to the living room. It contained a water-spotted stand of neglected African violets, a treadle sewing machine with a clove-studded dried orange tucked in one of its small oak drawers, a large dining room table and chairs, and a handmade oak China cabinet Grandma had purchased for ten dollars with the money she made selling eggs.
When Grandma made Sunday dinner for our extended family it was served at noon. Grandma removed elegant pieces of stemmed glassware and individual salt cellars from the cabinet and set the dining room table with her good silverware. As we passed roasted chicken with gravy, noodles, and side dishes, Grandpa arrived late (he was known for having “girlfriends”), threw his work cap in the corner, and took his seat at the head of the table.
Only now do I realize how little Grandma wasted. Usually, she cooked one of her own chickens on Sunday, but she occasionally made a pork roast. After the meal, any scraps of meat were set aside, combined with corn meal mush (I can only imagine her reaction to polenta recipes in upscale restaurants) and baked in a loaf pan. For breakfast the next day, she fried slices and we covered them with butter and syrup. They were delicious.
Over time, and with deaths and disagreements, our extended family grew smaller, and we began eating all our meals in the large kitchen. The food was still delicious. One time, Grandma asked how everything tasted. Grandpa was the only one who didn’t answer. She stared at him, and he finally grumbled, “If anything’s not good, I’ll let you know.” Already showing signs of Parkinson’s, he poured a bit of his coffee into a saucer with shaky hands, and leaned down to slurp it.
Eventually, an old couch was jammed into a corner of the dining room, next to the china cabinet. It became my reading space when I visited. Now, as I sit down to read on my own sofa, I look at that same cabinet on the front wall of my living room in Oberlin, just two hours away from where Grandma lived. I have covered the top with family photographs.

Grandma taught me how to tie my shoes–we were both left-handed–after everyone else had given up; gave me my first sip of coffee, strong but cut with generous portions of sugar and thick cream; slipped me some of her beer while we watched Gunsmoke. As I got older and visited less, we wrote letters.
Shortly after my twenty-first birthday, Grandma and I walk in her back yard. We stop under the hot sun to admire the clumps of purple, yellow, and white miniature pansies that flourish in the crumbling foundation of an old shed. I started college three years late; I tell her I am overwhelmed and don’t think I can do the work. She is quiet, removes a flowered hanky from her apron pocket, pats her damp forehead and the back of her neck.
As we start slowly up the steps to the relative cool of the house, I link arms with her. I brush the cool copper of the bracelet she always wears because she believes it helps her arthritis. Her fingers are crooked, as mine are now. As I write this, I touch the copper cuff bracelet I bought years ago but have never worn. I keep it on my desk as a reminder of Grandma, and I wonder what happened to the soft, linked one she always wore.
I open the back door with my other hand. Grandma suddenly stands as straight as she is able and says firmly, “You stay in school.” She adds this, which I will hear her say more than once: “You need to be able to make your own money.”
…
After I’ve finished graduate school, married, and had a child. After Grandpa, who spent years in a nursing home with Parkinson’s, has died. On what will turn out to be the day my dad, her son, dies, Grandma moves into an assisted living facility. With Dad being ill, no one has had the time to take Grandma to see the place prior to moving in. She’s been calling me several times a day, anxious about the change.
She surveys the room: her favorite chair with an afghan she made folded over the back; her dresser, its top covered with a lacy scarf and family photographs, including several of my daughter; a large window that looks out on gardens; the new spread my mom placed on her bed that morning; a private bath.
She leans close to me and whispers, “Oh, Melissa, this is beautiful. I was afraid it would be like the poor house.”

Melissa Ballard has written essays for The Brevity Blog, Belt, Berea College magazine, and other publications. She is currently working on a book-length collection of essays about the women in her Northern Appalachia family.
Like this post? Want more? Comment below or on my FB page. And please share with your friends and social network.
Are you a Rust Belt writer interested in seeing if your own post, or author interview, or book review might be right for Rust Belt Girl? Hit me up through this site’s contact function.
Check out my categories above for more guest posts, interviews, book reviews, literary musings, and writing advice we can all use. Never miss a post when you follow Rust Belt Girl. Thanks! ~Rebecca